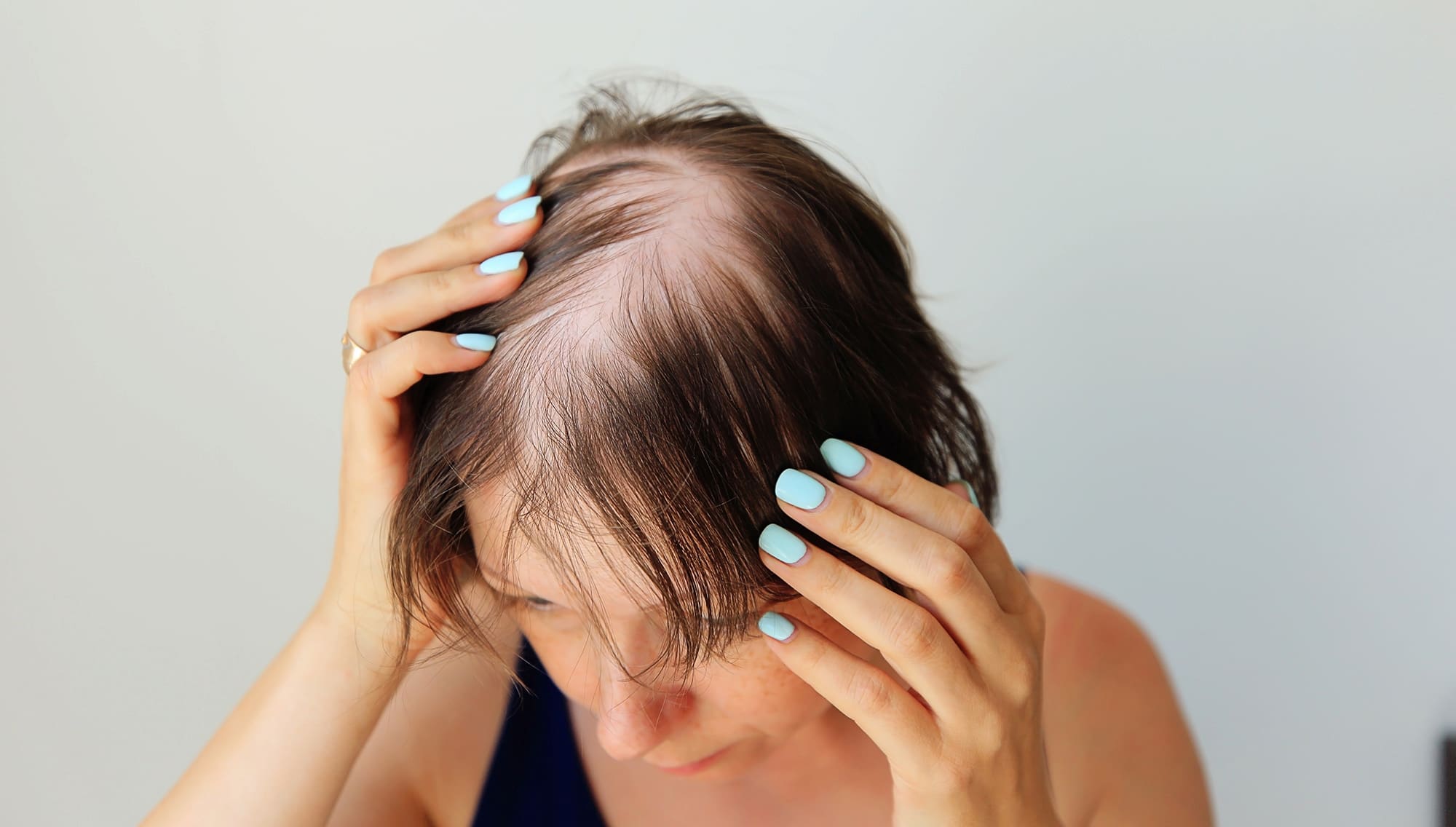
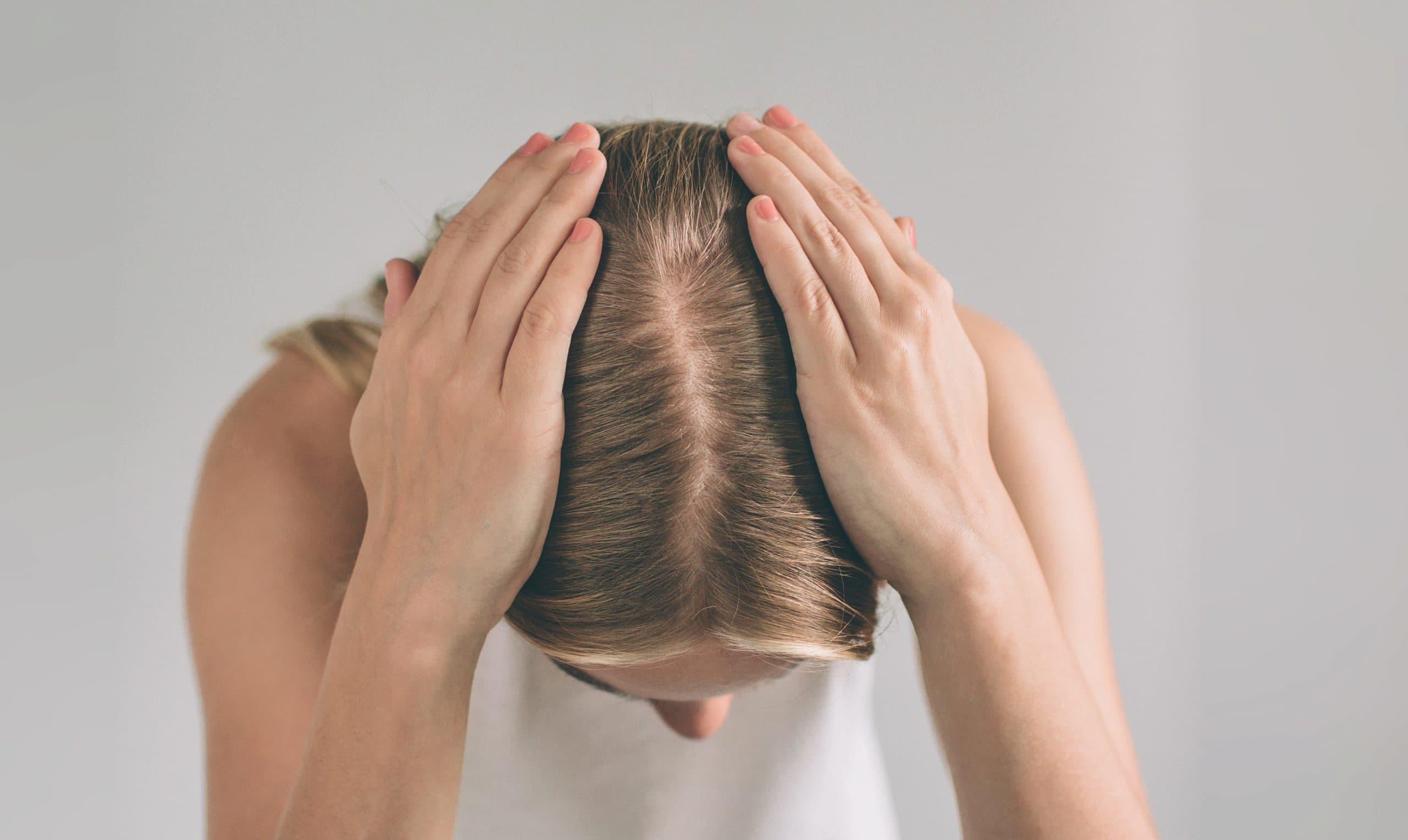
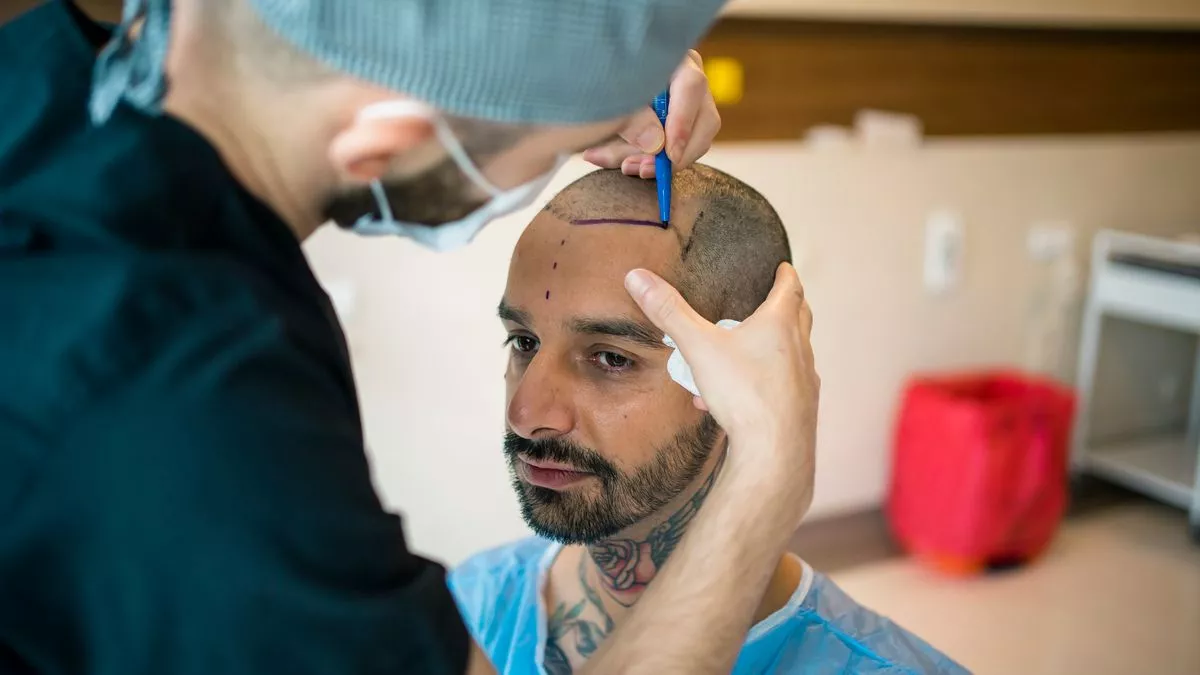
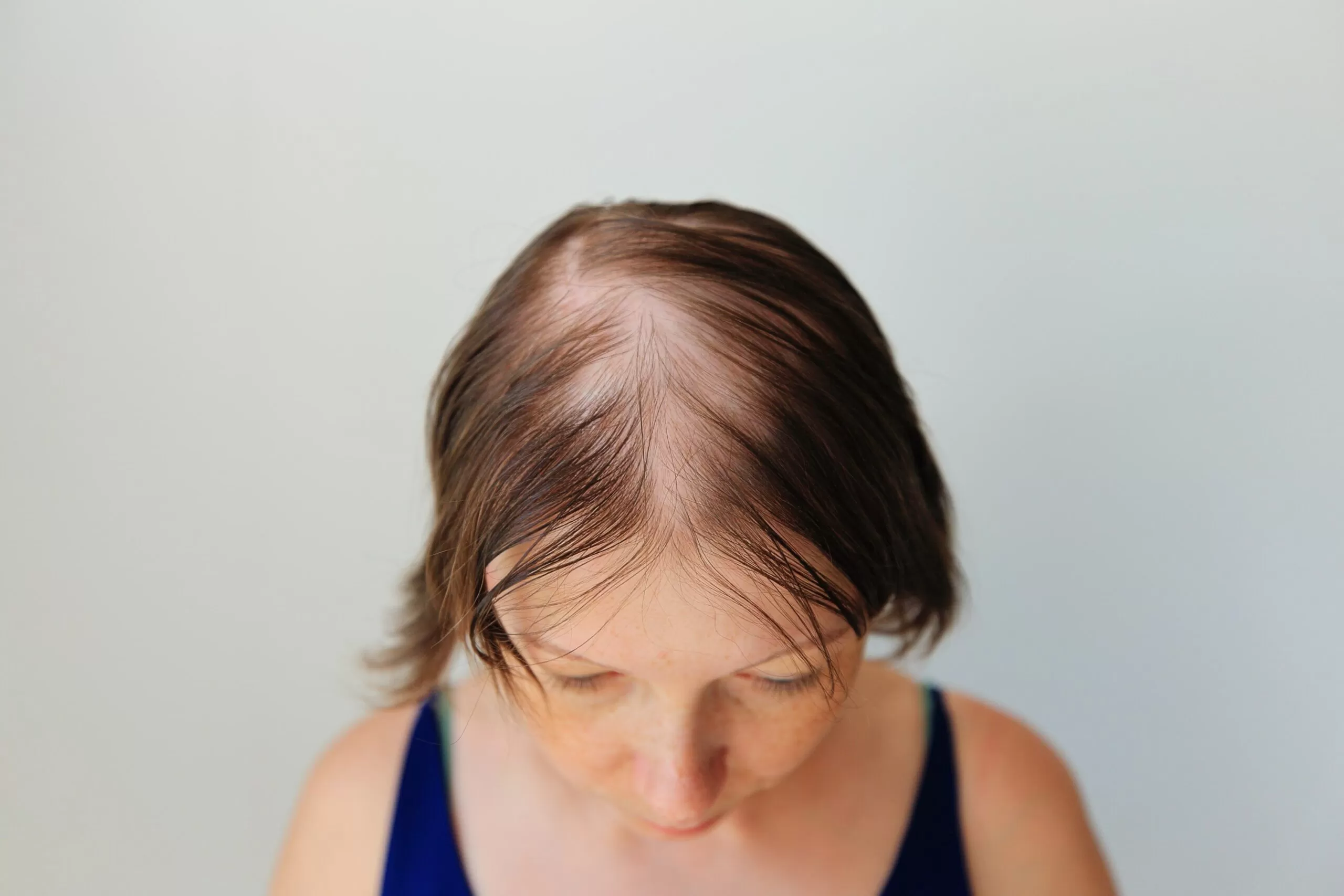
The Ludwig Scale is a key international classification system for female hair loss, used to determine the degree of androgenetic alopecia in women. Unlike male baldness, female hair loss is diffuse and manifests as uniform thinning in the central part of the scalp. With the help of the Ludwig Scale, a doctor can accurately determine the stage of alopecia, assess hair density, and develop an optimal treatment plan.
Why Women Lose Hair: Main Causes
Hair loss in women can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause, polycystic ovary syndrome)
- Genetic predisposition
- Endocrine system disorders
- Stress and emotional overload
- Vitamin and micronutrient deficiencies
- Poor scalp circulation
- Aggressive hair care, chemical coloring, styling
In most cases, androgenetic alopecia in women develops gradually. Therefore, early diagnosis is crucial for maintaining hair density.
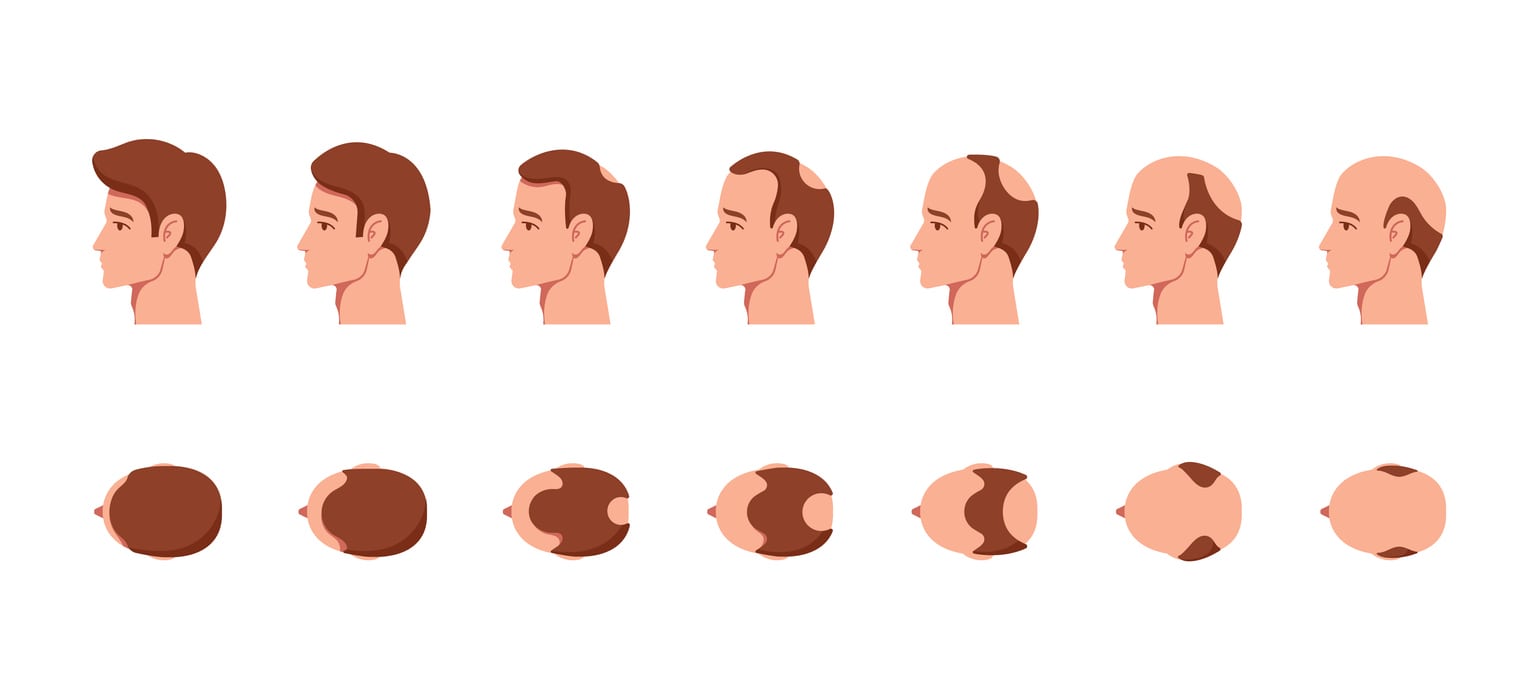
Stages of Hair Loss According to the Ludwig Scale
The Ludwig system consists of three main stages that reflect the progression of female hair loss:
Stage I
Mild diffuse thinning in the central part of the scalp. The parting becomes wider, but overall hair density remains satisfactory. This is the best time to start treatment.
Stage II
Noticeable loss of density — the parting widens along its length, and the hair becomes visibly thinner. Progressive diffuse hair loss is evident.
Stage III
Significant thinning in the crown area, with the scalp clearly visible. At this stage, medical treatment alone cannot restore volume — hair transplantation is often recommended for women.
Comparison Table of Stages According to the Ludwig Scale
Stage I
Signs: Mild thinning, wider parting
Recommended Methods: Medication therapy, mesotherapy, PRP
Stage II
Noticeable density loss, diffuse shedding
Recommended Methods: Combined treatment, injection methods
Stage III
Signs: Severe thinning, visible scalp in the central area
Recommended Methods: Hair transplantation + maintenance therapy
How Female Hair Loss Is Diagnosed
Clinics use the following diagnostic methods:
- Trichoscopy and dermatoscopy
- Hair density and diameter testing
- Laboratory tests (hormones, vitamins, ferritin)
- Photo documentation of progress
Accurate diagnosis allows physicians to distinguish androgenetic alopecia from temporary forms such as telogen effluvium.
Treatment Methods for Female Hair Loss
Method: Medication therapy
When Applied: Stage I–II
Advantages: Normalizes hair growth
Method: PRP therapy / Mesotherapy
When Applied: Stage I–II
Advantages: Improves blood flow and nourishment
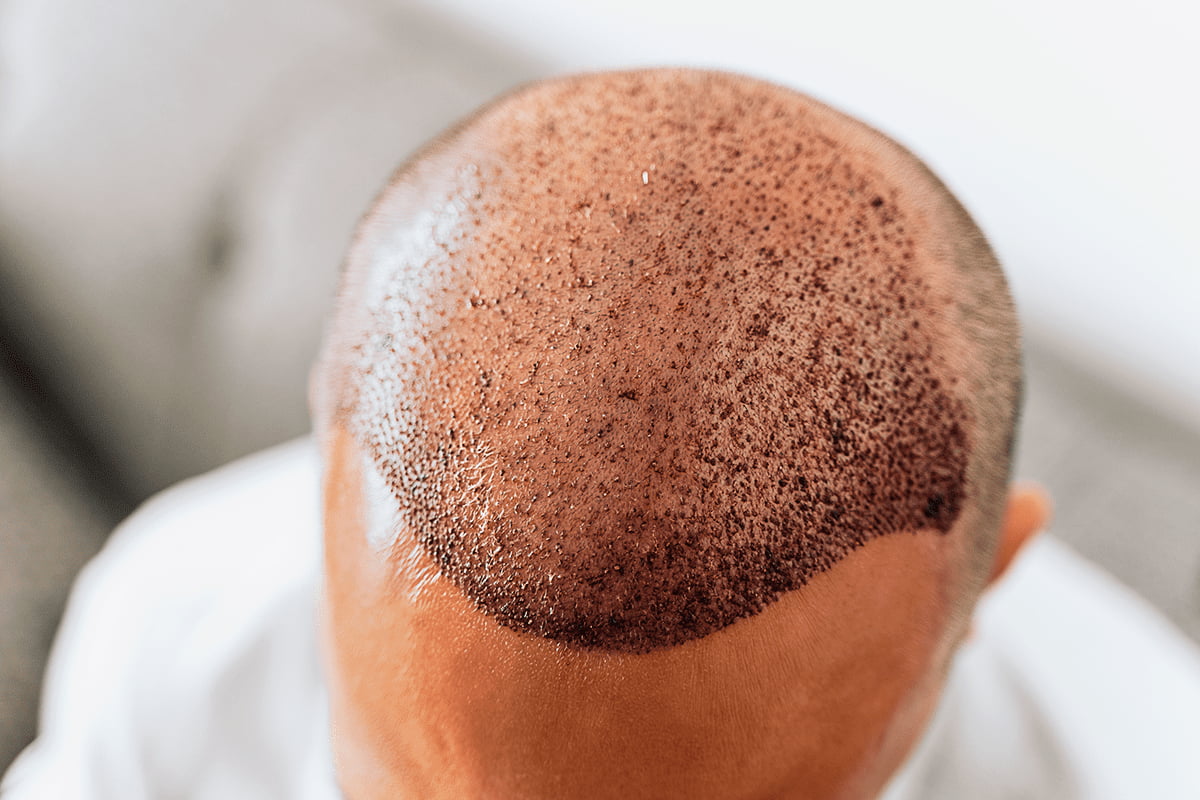
Method: Hair transplantation
When Applied: Stage II–III
Advantages: Restores density in thinning areas
At early stages, the process can be stopped and most hair preserved, while in advanced cases, transplantation provides the most predictable and long-lasting results.
Specific Features of Hair Transplantation in Women
Unlike men, women typically:
- Do not have large bald patches but show diffuse thinning
- Need to preserve parting density
- Require a maximally natural aesthetic result
Modern techniques (especially FUE) allow follicular transplantation without scarring, with a short recovery period and natural appearance.
Why Choose MHT Clinic
MHT Clinic specializes in the treatment of female hair loss and hair transplantation in Ukraine, using advanced technology, medical protocols, and a personalized approach. We help restore hair density even in complex cases of alopecia.
Conclusion
The Ludwig Scale is a fundamental tool for assessing the degree of female baldness and selecting the proper treatment. The earlier therapy begins, the higher the chances of preserving hair, restoring volume, and preventing significant thinning.
If you notice changes in your parting, reduced volume, or excessive shedding — contact the specialists at MHT Clinic.